Safety Audit in any Organization

Volume 4, Issue 3, July – Sept. 21
Safety Audit in any Organisation
Shahnawaz Rampuri
PhD (Scholar), Arunodya University – Arunachal Pradesh
Email id: shahnawaz.rampuri2@gmail.com
Abstract
Industries are major sources of economy development of country and create employment opportunities. Industries have positive & Negative impacts. Negative impacts arises due to not follow safety Rules, Procedures & guides. Hazard identification is major parameter to control work place risk. Safety Performance helps to Knows actual condition of organization, identify potential sources of harm and control them. Several Techniques & Method use to measure organisation safety performance, Examine Existing system and seek opportunities to improvement Safety Management System in which one is Technique is safety Audit. This Paper is very helpful to know effective method to conduct Safety Audit and measure Safety Performance. Safety Performance helps to know basic gaps of organization where needs possibility of improvement.
KEYWORD: Safety Audit, Non-Conformance identification Techniques, Seeking Opportunities to improve OHSMS, Accident Prevention, Risk control.
Purposes
- To check & verify Safety system of organization that are Fulfilling or meeting legal requirements or not
- Examine existing safety system of organization to know deficiency & work to improve safety system
- To Identify potential sources of harm, See their risk & recommending to organization to control such risk
- To determine Non-conformity or gaps and Seek opportunities to improve organization
Safety performance
Statutory provision of safety audit
- The Occupational Safety, Health & Working Condition Code 2020, Section 37, Third Party Audit & Certification
- Manufacturer Storage, Import of Hazardous Chemical Rules 1989, Rule 10, SAFETY REPORTS 1 [AND SAFETY AUDIT REPORTS], Need to conduct safety Audit Report by occupier once a year and forward a copy of audit report.
- Respective State rules such asMaharashtra Factories (Safety Audit) Rules, 2014
- Published vide Notification No. FAC. 2012/C.R.278/Lab- 4, dated 24.2.2014
- The IS 14489:2018, Audit Frequency, Conduct Internal Safety Audit in a one Year & External Safety Audit in a Two Year
1. Introduction
Safety Audit is important parameter that use to identify potential sources of harm or situation of any organization to control Risk in any organisation. In Industries Several potential Sources of harm available, latter that results accident.
In Simple Safety Audit is detailed examination of any organization that use to measure safety performance, identify to existing gaps and seeks for improvement. Safety Audit help to improve organization Safety Performance. Effective Safety System always help to control work place risk and Prevent accident. Accident always effect to business of any organization. Accident cost are two types Direct & Indirect Cost. Indirect Cost are several times more than direct cost. Accident always create Negative impacts. This results to earning capacity of injured family and loss of reputation of organization. Safety Audit effectiveness depend on competence of Auditor.
As Per IS 14489:2018, Internal Audit should be Conducted Annually & External Audit should be conducted once in Two year. In Safety Audit, Auditor identify the gaps of existing system and seek opportunities for improvements. Auditor Submit Report to Auditee organization for implementation of Recommendation to ensure safe work place and fulfill compliance obligation.
2. Advantage of Safety Audit:
- They Highlight Potential Problem of organisation
- Increase employee awareness
- Enhance your company Credential
- Save Organisation Money
- They may be viewed by regulatory agency
- They will offer Knowledge & Validation
- They will be offer Objectivity
- They offer greater result accuracy
- They can Lower your business impacts
3. Types of Safety Audit:
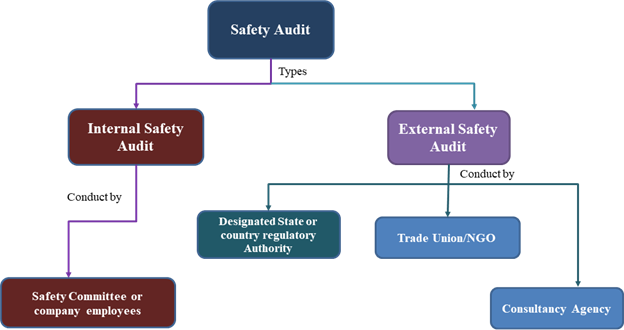
Fig. 1
4. Auditor Attribute
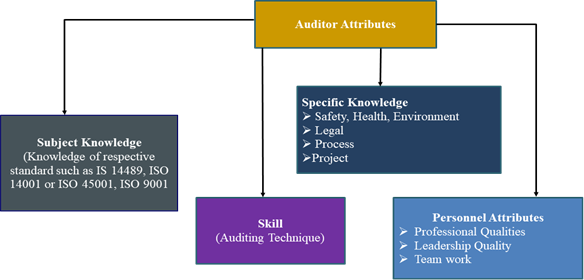
Fig. 2
5. ISEI-Audit Procedure
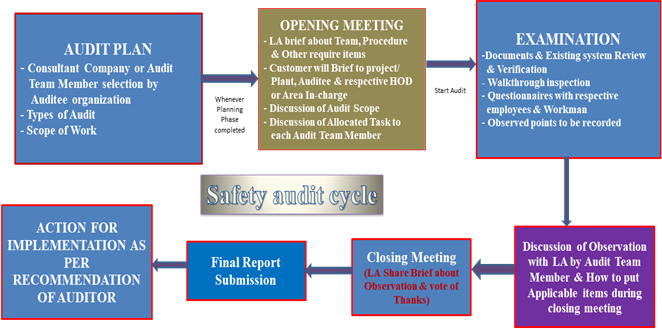
Fig. 3 A
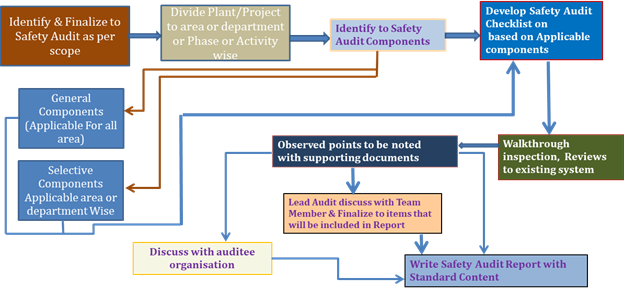
Fig. 3 B
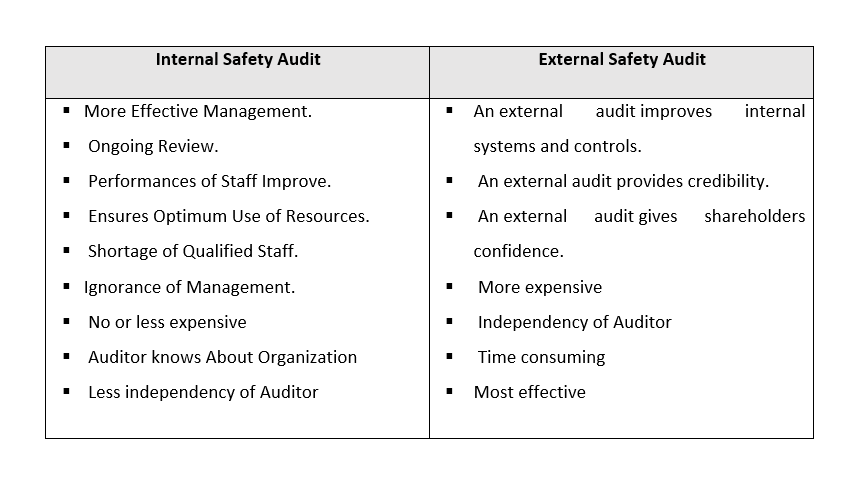
6. Internal Safety Audit V.S External Audit
7. Element that Check during Safety Audit
Element depends upon Nature of Organisation. Major No. of Organisation such as Safety Policy, Organisation chart, ERP, Training & Record are application of Organisation. Few Elements varies on based on Nature. Few Major elements of Safety Audit area.
- Safety policy
- Safety organization chart
- Competency & Skill of Safety Personnel
- Record of defined Role & Responsibilities
- Training records including safety induction, Tool box Talk and other applicable Training
- Record of plant/Project safety inspections
- Record of Accident investigation reports including Near Miss
- Near miss, Dangerous occurrences & Accidents statistics and analysis
- Examination & Record of tested equipment, Tools, Tackles and structures as per statutes
- Safe operating procedures for various operations
- Work Permit Program & Record of work permits
- Record of monitoring of flammable and explosives substances at work place
- Medical records of employees
- Fire detection and firefighting equipmentmaintenance and testing records.
- Industrial hygiene surveys records such as noise, ventilation and levels, illumination levels, airborne and toxic substances, explosive gases
- Material safety data sheets
- Record of Lock out/ Tag out System
- Safety Manuals, Safety Management Plan (SMP) & Tool Box Talk Manual
- Role & Responsibility Clear Defined and its Record
- Motivational Scheme Program & its Record
- Record of HIRA & JSA
- Environmental Clearance from CPCB/CPCB if Applicable
- On-site emergency plans and record of Mock Drills
- MOU with outside agency or organization to tackle emergency
- Records of effluent discharges to the environment
- Housekeeping inspection records
- Minutes of safety committee meetings
- Approval or Permission from of plant, layouts from statutory authorities
- Records of any modifications carried out in plant or structure or building
- Shut down maintenance procedures
- Service inspection manuals, records & Procedure record.
- Safety budget
- Inspection books and other statutory records
- Records of previous audits
- Safety in transportation of hazardous substances
- PPE’s Issued Register and Inspection Record
- Record of Minutes of Meeting & their compliance status
- Existing welfare Amenities
- Safety Reporting system & record of past year report
- Govt. Permission Letter to Operate Plant or Project site
- Waste Management Plan, Record of Waste Generation & disposal
- Calibration and testing records
- Motivational Scheme Program & Its Record
- Record of workplace Environmental monitoring Report
- Work permit program & Records etc.
8. Point Remember during Safety Audit
- Always Take support with Auditee or respective area in-charge to
- know details about area or require items
- Conduct walkthrough with Audit checklist
- Respective Legislation should be linked with Checklist
- Check all components of Safety Audit
- Collect evidence of observation
- Always observe to conformance as well as Non-conformance
- Conduct interview with site/ department workmen or employees
- Write observation clearly with location/ Section wise and equipments name
- As Per observation, evaluate to potential impacts and write it in note book
- At end of Audit share all observed items with Lead Auditor
9. Role Of Auditee Organization To Complete Successful Effective Safety Audit
- Senior Mgt. of Auditee Organization should inform to
- respective Head/Area incharge of their plant/ project about audit schedule, scope & support to audit team.
- Auditee Organization should provide adequate resources to Auditor if require.
- Auditee Organization should share correct information to Auditor as require or ask by auditor.
- Confidential document or information when ever sharing to Auditor, Auditee Organization should inform proactively.
- If any issue with Safety System of Auditee Organization, Need to share with Auditor
- Respective Head/ Area in-charge should share process flow details or area summary to Auditor when Auditor ask
- Auditee should show all record, Procedures & program to Auditor when Auditor ask etc.
10. Role Of Auditor To Complete Successful Effective Safety Audit
- Keep details Knowledge about Applicable Element of Safety System/ OHS system where safety audit is to be conducted
- Auditor should know Emergency Plan content and other similar items for effective review
- Auditor should be more observant/ vigilant during Audit
- Auditor must be effective skill to deal with Auditee
- Auditor should verify to available documents, Procedure or system with site to know their implementation status.
- Question with HOD/ Area in-charge and respective employees including
- Auditor Should keep List of Safety System Element & Checklist during visit at site or review to system.
- In case of any Major observation or issue immediate inform to Auditee Organization
- Lead Auditor will co-ordinate regularly to conduct audit
- Auditor must be Complete Safety Audit with schedule time & submit report within time frame
11. Points To Be Remember During Audit
- Always Take support with Auditee or respective area in-charge to know details about area or require items
- Conduct walkthrough with Audit checklist
- Respective Legislation should be linked with Checklist
- Check all components of Safety Audit
- Collect evidence of observation
- Always observe to conformance as well as Non-conformance
- Conduct interview with site/ department workmen or employees
- Write observation clearly with location/ Section wise and equipments name
- As Per observation, evaluate to potential impacts and write it in note book
- At end of Audit share all observed items with Lead Auditor
12. Conclusion:
- Safety Audit help to control work place risk, fulfilling compliance obligation & increase organization reputation.
- Safety Audit is effective method used to examine existing system & seek opportunities to improve organization Safety Performance
- Implementation of recommendation is responsibility of Auditee Organization.
- Auditor should keep Knowledge of IS 14489, ISO 45001, ISO 14001, ISO 9001 & Respective state or country rules to conduct effective safety audit.
- Organization should prepare Safety Audit Program & based on this they should conduct safety Audit (Internal/External) to get Organization safety related objective.
- In Safety Audit Program, Include all Applicable parameter including Safety System element of respective Organization.
- In case of external Audit, Auditor should submit draft report to Auditee Organization first and submit final report whenever Auditee organization confirm.
References:
- The Occupational Safety, Health & Working Condition Code 2020
- Manufacturer Storage, Import of Hazardous Chemical Rules 1989,
- Maharashtra Factories (Safety Audit) Rules, 2014 Published vide Notification No. FAC. 2012/C.R.278/Lab- 4, dated 24.2.2014
- The IS 14489:2018
- ISEI Manuals
